Every year, artificial intelligence models continue to grow larger and more powerful. These systems can perform startling tasks, such as answering queries, writing text, and even thinking. However, one concern remains: how do they retain and apply knowledge within? For many academics, the inner workings of these models are like a black box. Ensuring safety, fairness, and openness becomes more challenging when things are unclear.
New methods are being explored to address this issue. The Sparse AutoEncoder is one technique that looks promising. This program doesn't just make files smaller; it also makes it simpler to see hidden patterns. It helps show structures that people can understand by making neuron activity simpler and more specific. This method offers new insights into understanding how modern AI systems operate.
Superposition makes it hard for neural networks, especially large language models, to be understood. Superposition happens when there aren't enough neurons to encode all of the features. In these situations, one neuron has to store information on more than one thing that isn't related to the other. For instance, one neuron might respond to both cats and car wheels, which makes it difficult to determine its meaning. Researchers struggle to discern what the model truly learns due to this overlap.
Superposition allows models to store a large number of features in a small space, but also makes things less clear. These problems worsen as networks become larger and more complex. If something isn't easy to understand, it becomes more challenging to ensure it's fair, safe, and open. For academics and developers, superposition illustrates the trade-off between ease of understanding and efficiency. The issue necessitates innovative techniques capable of disentangling overlapping features, hence providing a clearer perspective on the internal organization of knowledge within models.
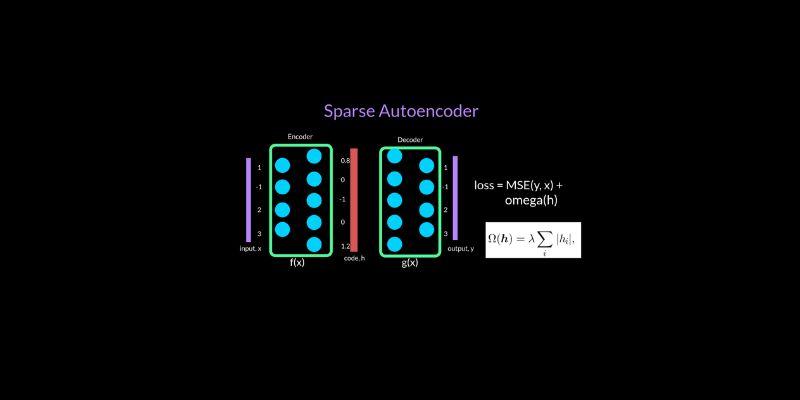
Sparse AutoEncoders are a unique kind of autoencoder that makes things easier to understand by making them less dense. Sparse autoencoders leave most neurons dormant, while dense ones activate many neurons at once. Only a limited number of neurons are activated for each input, which makes them specialize. This division reduces overlap and increases the likelihood that each neuron will represent a single, understandable concept.
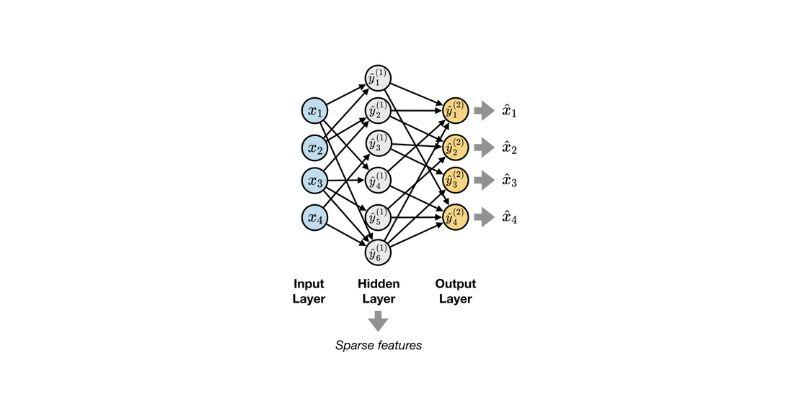
A sparse autoencoder consists of two primary components: the encoder, which compresses the data, and the decoder, which reconstructs it. The model learns useful characteristics instead of trivial compression by introducing a sparsity constraint during training. The method is similar to how the human brain efficiently analyzes information using sparse representations. Sparse autoencoders facilitate the identification of hidden patterns in complex models, making them particularly useful in real-world applications. They find traits that fit into categories that people can comprehend, which makes analysis easier.
When designing and training a sparse autoencoder, it is essential to strike a balance between making it smaller and easier to understand. The model contains an encoder that transforms input activations into a new feature space and a decoder that reconstructs the original input. Researchers apply a penalty to discourage excessive neuron activation, ensuring sparsity. L1 regularization is a typical choice since it limits the number of neurons that fire. The autoencoder utilizes both reconstruction loss and sparsity loss to ensure that the output is accurate and easy to interpret.
In practice, training involves obtaining activations from a trained model, such as the hidden layers of a neural network, and then feeding those activations into the autoencoder. The aim is not to enhance the performance of the original model but to conduct an analysis. Researchers can get a sparse representation where features become disentangled by carefully adjusting the parameters. This training approach is easy to use yet highly effective, making it a valuable way to learn about complex systems.
One of the key advantages of sparse autoencoders is that they can help distinguish features in language models. Think of a toy model that learned from words like "cat," "dog," "not cat," and "AI assistant." In a dense representation, neurons can overlap, which means that animals and machines, as well as positive and negative concepts, can be mixed. You can map these activations onto a higher-dimensional, sparse space with a sparse autoencoder, where features are clearly separated. One neuron might be good at recognizing animals, while another might be good at distinguishing between technical ideas like robots and assistants.
More neurons might be responsible for distinguishing things like "not dog" or "not cat." This disentangling creates patterns that are easy for people to understand and categorize. Although the toy model is simplistic, it demonstrates how sparse autoencoders can extract useful features from more complex systems. By making each idea clear, they help researchers understand how large language models organize knowledge. This clarity allows researchers to evaluate, explain, and improve model behavior.
When you examine the interpretable features that sparse autoencoders produce, you can see their utility. Neurons no longer respond to irrelevant patterns; instead, features begin to align with concepts that make sense. For instance, in a toy model, one feature would show animals, another might show technology, and a third might show negation. These results demonstrate how sparse autoencoders transform hidden structures into categories that people can comprehend.
This approach helps researchers determine what information a model actually stores. Interpretability is not only theoretical; it offers tangible advantages. Developers can monitor bias models, identify harmful behaviors, and make things fairer by utilizing interpretable characteristics. They also make debugging easier because you can find the neurons that are causing problems. Sparse autoencoders are not perfect, but they are a big step toward understanding massive models.
Sparse autoencoders represent a significant step in making complex AI models more comprehensible. They allow neurons to convey clearer and more useful ideas by reducing overlapping messages. This change makes it easier for scientists to access information stored in large systems. Interpretable characteristics also make real-world programs safer, fairer, and easier to fix. There are still problems to solve, but the advancement is enormous. Sparse autoencoders demonstrate that we can overcome hidden complexity and progress toward greater openness. If you're concerned about the future of AI, these tools are great for building confidence and understanding in advanced models.

Failures often occur without visible warning. Confidence can mask instability.

We’ve learned that speed is not judgment. Explore the technical and philosophical reasons why human discernment remains the irreplaceable final layer in any critical decision-making pipeline.

Understand AI vs Human Intelligence with clear examples, strengths, and how human reasoning still plays a central role

Writing proficiency is accelerated by personalized, instant feedback. This article details how advanced computational systems act as a tireless writing mentor.

Mastercard fights back fraud with artificial intelligence, using real-time AI fraud detection to secure global transactions

AI code hallucinations can lead to hidden security risks in development workflows and software deployments

Small language models are gaining ground as researchers prioritize performance, speed, and efficient AI models

How generative AI is transforming the music industry, offering groundbreaking tools and opportunities for artists, producers, and fans alike.
Exploring the rise of advanced robotics and intelligent automation, showcasing how dexterous machines are transforming industries and shaping the future.

What a smart home is, how it works, and how home automation simplifies daily living with connected technology

Bridge the gap between engineers and analysts using shared language, strong data contracts, and simple weekly routines.

Optimize your organization's success by effectively implementing AI with proper planning, data accuracy, and clear objectives.