Vision language models are AI models that can simultaneously understand both images and text. They are like Large Language Models, but with the extra ability to see. This feature makes them powerful tools for solving tasks such as captioning, object detection, and visual question answering, where the model examines an image and provides an answer to a question about it.
In real life, this can be very useful, like helping doctors analyze X-rays with written reports or even supporting people with vision impairments by explaining what's in front of them. To achieve better results, you can also try different promotional methods. If you're unsure how to prompt VLMs to perform these tasks, you can find some simple strategies for promoting vision language models here. So, keep reading!
Prompting vision language models means providing the model with instructions (text) and, often, an accompanying image. It enables the model to determine its actions. The key strategies for prompting vision language models include few-shot prompting, zero-shot prompting, chain-of-thought prompting, and object detection-guided prompting. Let’s learn about these strategies in detail below:
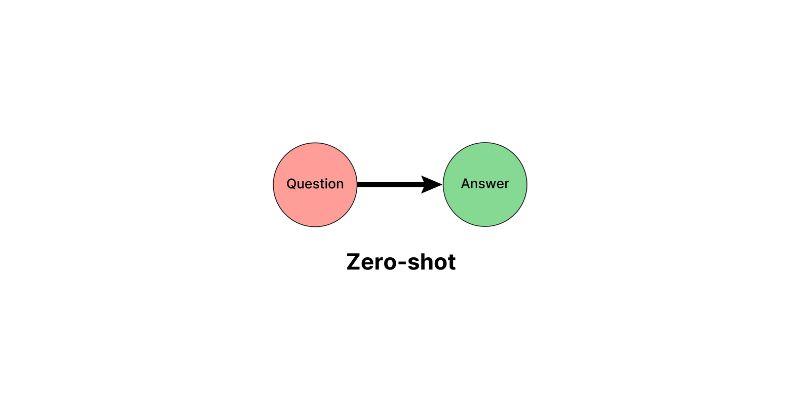
Zero-shot prompting is a method of utilizing LLMs without providing them with example outputs. The model only gets an instruction and some input. It will produce the correct output based on what it has learned during training. The model utilizes its pretraining knowledge to comprehend new tasks without requiring examples. The prompt usually includes components like:
Zero-shot prompting offers several strengths that make it valuable in various situations. One of the most significant advantages is that it is extremely user-friendly. You do not need to collect or prepare example outputs before working. It is especially useful when there is little or no task-specific data available. However, zero-shot prompting also has essential weaknesses. Its performance can vary significantly, especially when the task is challenging, because the model has no examples to follow. It depends heavily on the knowledge it gained during pretraining. If the model was not exposed to similar tasks or information during that stage, its answers will be inaccurate or weak.
Few-shot prompting demonstrates an AI model with a limited number of examples of a task, allowing it to learn how the task operates. Instead of giving many training data, you will provide just a few "example input → example output" pairs. After that, you can ask the model to produce the output for a new input. When tasks lack a substantial amount of labeled data, few-shot prompting is particularly useful. It helps models such as Meta's LLaMA and OpenAI's GPT-3 and GPT-4. Here's how it works simply:
Few-shot prompting offers several advantages, including the ability to work with AI even when large labeled datasets are not available. It makes it useful in situations where gathering training data is expensive or time-consuming. Another benefit is that it gives more control over the output style, format, or structure. Despite these strengths, few-shot prompting has some clear limitations. The quality of the examples used is essential. If the examples are poor and unclear, the model will generate weak or incorrect results. Another challenge is that including examples in the prompt takes up space in the model's context window. For large or multiple examples, the prompt can quickly become too big, leaving less room for new input data. If the model has not seen similar tasks during training, the presence of examples alone will not be enough to guarantee accuracy.
Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting is a method that helps LLMs solve complex problems by guiding them to think in steps. Instead of asking for a quick, direct answer, CoT asks the model to break the problem into smaller pieces. It presents its reasoning and then arrives at the final answer. When problems are complex, like math word problems, logic puzzles, or multi-stage questions, it asks the model to "explain your thinking step by step" and leads to better, more accurate answers. CoT prompting is effective because of several factors.
This strategy incorporates an additional component, object detection. The idea is to detect or identify objects in the image. Then feed that information into the VLM to help it generate captions. The detected objects can help the VLM focus on what matters in the image. The technique works roughly like:
Object detection-guided prompting doesn't constantly improve simple image captioning of very simple images. However, it becomes powerful for more complex tasks (like document understanding, layout, scenes with many items), where knowing where objects are helps the model produce better, more useful captions.
Vision Language Models bring together the strengths of both text and image. It can be used to answer questions about images, create accurate captions, or support tasks in healthcare, among other applications. VLMs open the door to more intelligent and more useful AI systems. We can guide these models to deliver better results by learning how to prompt them effectively.

Failures often occur without visible warning. Confidence can mask instability.

We’ve learned that speed is not judgment. Explore the technical and philosophical reasons why human discernment remains the irreplaceable final layer in any critical decision-making pipeline.

Understand AI vs Human Intelligence with clear examples, strengths, and how human reasoning still plays a central role

Writing proficiency is accelerated by personalized, instant feedback. This article details how advanced computational systems act as a tireless writing mentor.

Mastercard fights back fraud with artificial intelligence, using real-time AI fraud detection to secure global transactions

AI code hallucinations can lead to hidden security risks in development workflows and software deployments

Small language models are gaining ground as researchers prioritize performance, speed, and efficient AI models

How generative AI is transforming the music industry, offering groundbreaking tools and opportunities for artists, producers, and fans alike.
Exploring the rise of advanced robotics and intelligent automation, showcasing how dexterous machines are transforming industries and shaping the future.

What a smart home is, how it works, and how home automation simplifies daily living with connected technology

Bridge the gap between engineers and analysts using shared language, strong data contracts, and simple weekly routines.

Optimize your organization's success by effectively implementing AI with proper planning, data accuracy, and clear objectives.