Neural networks speak in probabilities, not certainties, and those numbers can sound more confident than they deserve. A model may hand you a shiny score while guessing on thin evidence because softmax always crowns a winner. That gap between reported confidence and real correctness is model uncertainty.
Thresholding adds a simple gate on top of scores so shaky predictions do not flow through. Confidence is the top-class probability, and uncertainty is the risk that confidence and correctness do not match. Calibration is the step that makes scores line up with observed accuracy so thresholds actually mean what they claim.
High confidence does not guarantee high accuracy because the training goal rewards correct labels more than honest probabilities. Scores drift upward and look bolder than they should. Thresholding helps filter weak calls, yet it works best after calibration.
When scores are honest, a cutoff of 0.8 behaves like eight correct predictions out of ten. Without calibration, the same number may pass many errors or block useful predictions. That mismatch wastes time and shakes trust, especially when teams rely on a single knob to control risk.
Temperature scaling is a tiny change with a big effect. You learn one temperature on a validation set, rescale logits, and leave the winning class untouched while straightening the reliability curve. Platt scaling adds a logistic link when the mapping needs shape, and isotonic regression follows the data with a flexible staircase that can capture quirks at different score ranges.
After any of these steps, a reliability diagram tells you whether predicted probabilities match observed accuracy by bins. When those points hug the diagonal, your scores speak truth, and a threshold becomes a clear decision rule instead of a guess.
A threshold should mirror the decision you care about. One path is to sweep the cutoff and choose the point that reaches a target precision, which keeps false positives contained when a wrong positive is expensive. Another path holds recall steady and accepts extra false positives when missing a true case hurts more than a false alarm.
Many teams go straight to cost. Assign numbers to a false positive and a false negative, compute expected cost at each candidate cutoff on the validation set, and choose the smallest value. That turns a heated debate into a transparent tradeoff you can document and review.
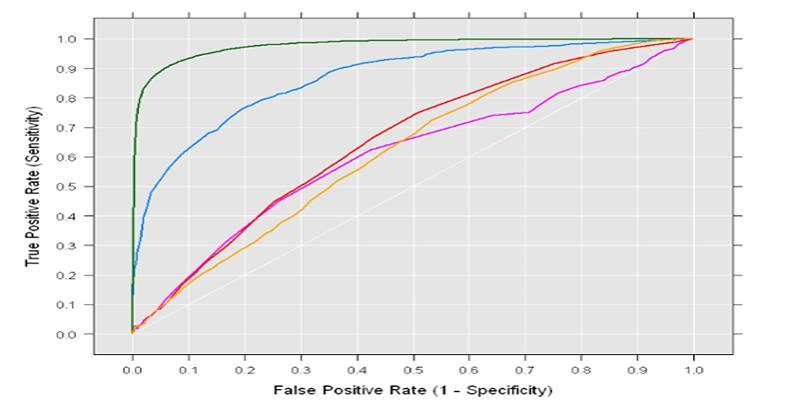
Accuracy can look fine while a minority class suffers. Precision and recall bring attention back to the positive class and expose the tradeoff you are actually making as the gate moves. By walking along the precision recall curve, you see how stricter or looser cutoffs reshape outcomes and where the knee sits.
ROC curves compare true positive rate with false positive rate and can be useful, though they often flatter models when negatives dominate. If you need a single summary during tuning, the F1 score blends precision and recall, but the full curve tells the richer story and keeps you honest.
A single global cutoff can punish rare classes that carry lower confidence even when they are correct. Class-wise thresholds offer a clean response. Pick a separate cutoff per class so rare labels keep useful recall while common labels stay precise.
Another route is class-wise calibration, so that a score of 0.6 for a rare label means the same thing as a 0.6 for a frequent one. Keep your validation split stratified when you tune, and confirm results on a second slice that mirrors production. Skipping these steps invites noisy thresholds that wobble once the model meets live data.
Not all mistakes hurt the same, and a good threshold should reflect that. Some false positives are a minor detour; some false negatives carry real pain. Turn that feeling into numbers. Multiply the false positive rate by its cost and the false negative rate by its cost, add them for each candidate cutoff, and choose the smallest total.
This simple step moves the debate from taste to tradeoff. People can disagree on costs, but once those are set, the threshold follows the math, and reviews become faster, calmer, and repeatable.
Confidence is only one clue. Monte Carlo dropout repeats forward passes with dropout active and reads the spread across runs. A widespread signals epistemic uncertainty, the kind that arises from limited knowledge rather than noisy measurements.
Deep ensembles average several independently trained models and often produce steadier probabilities that track outcomes better. You can fold these signals into your gate by checking entropy or variance along with the mean probability.
Data shifts, and score distributions shift with it, so thresholds need care after launch. Track acceptance rate, the share of predictions that pass the gate, and watch for spikes or drops that hint at drift. Add periodic labeled checks to measure live precision and recall, even if samples are small.
Refresh calibration when reliability bends, and confirm that class-wise behavior still matches targets instead of drifting away. When the gate needs moving, write down the reason, retest on a clean slice, and share the change. Small, steady upkeep beats emergency fixes.

Write down how you picked the threshold, and be specific. Record the date, the dataset slice, the metric target, the final cutoff, and the fallback path for low confidence cases. Note whether the threshold is global or class-wise and how often you refresh calibration.
Include the expected acceptance rate and a confidence band for precision so reviewers know what drift looks like. A short, human summary builds trust, speeds audits, and helps later changes stay reversible without confusion or long meetings.
Thresholding turns slippery confidence scores into a clear decision rule you can tune, test, and maintain with steady habits. With calibration in place, a chosen cutoff maps to the tradeoff you want, and class-wise tuning protects rare labels without flooding the rest.
Extra checks from entropy, variance, or ensembles add a safety net when inputs drift or new patterns appear. With active monitoring and plain documentation, the threshold becomes a transparent control knob rather than a guess, which keeps risky predictions out and lets strong calls pass.

Failures often occur without visible warning. Confidence can mask instability.

We’ve learned that speed is not judgment. Explore the technical and philosophical reasons why human discernment remains the irreplaceable final layer in any critical decision-making pipeline.

Understand AI vs Human Intelligence with clear examples, strengths, and how human reasoning still plays a central role

Writing proficiency is accelerated by personalized, instant feedback. This article details how advanced computational systems act as a tireless writing mentor.

Mastercard fights back fraud with artificial intelligence, using real-time AI fraud detection to secure global transactions

AI code hallucinations can lead to hidden security risks in development workflows and software deployments

Small language models are gaining ground as researchers prioritize performance, speed, and efficient AI models

How generative AI is transforming the music industry, offering groundbreaking tools and opportunities for artists, producers, and fans alike.
Exploring the rise of advanced robotics and intelligent automation, showcasing how dexterous machines are transforming industries and shaping the future.

What a smart home is, how it works, and how home automation simplifies daily living with connected technology

Bridge the gap between engineers and analysts using shared language, strong data contracts, and simple weekly routines.

Optimize your organization's success by effectively implementing AI with proper planning, data accuracy, and clear objectives.