The demand for privacy-preserving machine learning continues to grow, and federated learning sits comfortably at the center of that shift. Unlike traditional approaches where data is pooled into a central location, federated learning trains models right where the data is created—on devices or servers scattered across different locations. What makes this idea go from a research paper to actual code is a solid framework. That’s where Flower and Hugging Face come into play. Together, they form a duo that helps you build and train powerful models without sacrificing privacy or data locality.
Let’s break it all down, starting with the idea behind federated learning and then walking through how you can actually implement it using these tools.
In standard machine learning, all the data is sent to a central server where training takes place. It’s effective, but not always feasible. Think of healthcare records, mobile usage logs, or financial data. Sending all that sensitive information to one place raises all kinds of flags—privacy, regulation, security, and even bandwidth.
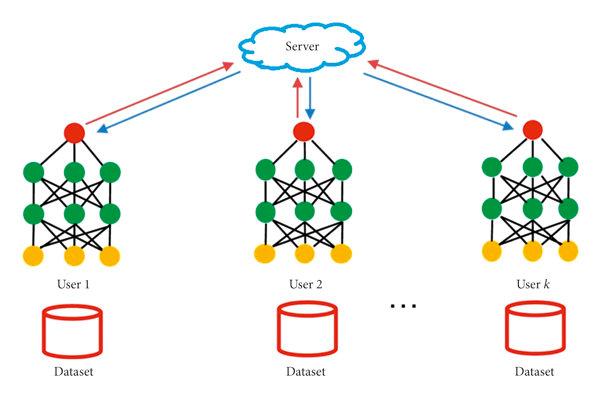
Federated learning flips that model. Instead of pushing the data to the model, it brings the model to the data. Each device or node trains a local version of the model using its own dataset. Then, only the updates (like model weights or gradients) are sent back to a central server. That server doesn’t see the raw data—only the insights gained from it. These updates are then averaged or aggregated, and the improved model is sent back out to the devices.
It’s collaborative learning without centralization. And when done right, it protects data, reduces risk, and still delivers results.
You might already know Hugging Face for its Transformers library—pretrained models that can be fine-tuned on tasks like text classification, summarization, or question-answering. It simplifies access to powerful architectures like BERT, RoBERTa, and DistilBERT, among others.
Flower, on the other hand, is built specifically for federated learning. It provides all the moving parts: client/server setup, communication protocols, model aggregation, and more. The real beauty lies in how customizable it is. Whether you're using PyTorch, TensorFlow, or even scikit-learn, Flower plays well with your codebase.
When you put the two together, you get a flexible federated learning pipeline that can support complex natural language tasks without having to reinvent the wheel.
Let’s walk through the steps to build a simple federated learning pipeline using Hugging Face models and Flower as the orchestration tool. We'll use PyTorch as the backend for this example, but Flower also supports TensorFlow.
Each federated client will have its own chunk of data. For simplicity, suppose you’re doing sentiment analysis using the IMDb dataset. You’ll split it across several clients. Each client keeps its own share and doesn't share raw data.
from datasets import load_dataset
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
dataset = load_dataset("imdb")
train_data, _ = train_test_split(dataset["train"], test_size=0.9)
client_data = [train_data[i::5] for i in range(5)] # Simulate 5 clients
Here, we'll pick a lightweight model to keep the training manageable. DistilBERT works well for this.
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForSequenceClassification
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("distilbert-base-uncased")
model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("distilbert-base-uncased", num_labels=2)
Each client handles local training and evaluation. Flower provides a NumPyClient base class that we can extend.
import torch
import flwr as fl
class IMDbClient(fl.client.NumPyClient):
def __init__(self, model, data):
self.model = model
self.data = data # This should be preprocessed
def get_parameters(self):
return [val.cpu().numpy() for val in self.model.state_dict().values()]
def set_parameters(self, parameters):
state_dict = dict(zip(self.model.state_dict().keys(),
[torch.tensor(p) for p in parameters]))
self.model.load_state_dict(state_dict, strict=True)
def fit(self, parameters, config):
self.set_parameters(parameters)
self.model.train()
# Local training loop here
return self.get_parameters(), len(self.data), {}
def evaluate(self, parameters, config):
self.set_parameters(parameters)
self.model.eval()
# Local evaluation logic here
return 0.0, len(self.data), {"accuracy": 0.9}
Each client will run its own version of this class with its own dataset slice.
The server handles coordination. It sends out the global model, collects updates, averages them, and sends the refined model back.
fl.server.start_server(
server_address="localhost:8080",
config=fl.server.ServerConfig(num_rounds=3),
)
Each client needs to connect to the server and run its own training session.
def start_client(data):
model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("distilbert-base-uncased", num_labels=2)
client = IMDbClient(model, data)
fl.client.start_numpy_client(server_address="localhost:8080", client=client)
# This would be called for each client in parallel
Large Transformer models can be a bottleneck when working with low-resource devices. It’s often better to use compact variants like DistilBERT or MobileBERT. These offer decent performance while keeping communication and memory overhead low.
One round of training can involve sending millions of parameters back and forth. Flower offers customization hooks to reduce how frequently updates are shared. You can also use techniques like quantization or sparsification to slim down the payload.
In some cases, you might not need to update the entire model. Freezing the backbone and only training the classification head can reduce complexity and make the process more efficient.
Federated learning enhances privacy, but it's not immune to attacks. Differential privacy and secure aggregation are advanced techniques you can integrate with Flower if security is a critical concern.

Federated learning no longer belongs solely in research papers. With tools like Hugging Face and Flower, it's possible to put real models into production without centralizing data. Hugging Face simplifies the modeling side, while Flower handles the coordination across nodes.
By following a modular approach, you can reuse models you've already trained and fine-tune them locally in ways that respect privacy. Whether you're working with a mobile device fleet or decentralized servers, this setup scales smoothly and respects the constraints that modern data privacy regulations demand.
While there are challenges—like managing model size, communication bandwidth, and update frequency—these can be addressed with smart choices in architecture and optimization. Hugging Face and Flower don’t remove the work, but they definitely make it more practical.

Failures often occur without visible warning. Confidence can mask instability.

We’ve learned that speed is not judgment. Explore the technical and philosophical reasons why human discernment remains the irreplaceable final layer in any critical decision-making pipeline.

Understand AI vs Human Intelligence with clear examples, strengths, and how human reasoning still plays a central role

Writing proficiency is accelerated by personalized, instant feedback. This article details how advanced computational systems act as a tireless writing mentor.

Mastercard fights back fraud with artificial intelligence, using real-time AI fraud detection to secure global transactions

AI code hallucinations can lead to hidden security risks in development workflows and software deployments

Small language models are gaining ground as researchers prioritize performance, speed, and efficient AI models

How generative AI is transforming the music industry, offering groundbreaking tools and opportunities for artists, producers, and fans alike.
Exploring the rise of advanced robotics and intelligent automation, showcasing how dexterous machines are transforming industries and shaping the future.

What a smart home is, how it works, and how home automation simplifies daily living with connected technology

Bridge the gap between engineers and analysts using shared language, strong data contracts, and simple weekly routines.

Optimize your organization's success by effectively implementing AI with proper planning, data accuracy, and clear objectives.